Preheating in an industrial furnace
Preheating refers to a targeted increase in material temperature before the actual process. This process is necessary in many areas of industry, research and trade in order to guarantee quality and protect the material of the tool and the workpiece.
Application examples for preheating
Tools or molds are often preheated so that the temperature difference in the process is not so high. The reasons for this are as varied as our customers’ processes. In some manufacturing processes, unheated tools would cause the surface of the material to cool down, resulting in a change in the microstructure, increasing wear or making processing more difficult.
For example, the workpiece is preheated during welding to optimize the end result. Preheating before welding means that the weld seam cools down more slowly and the hydrogen can escape.
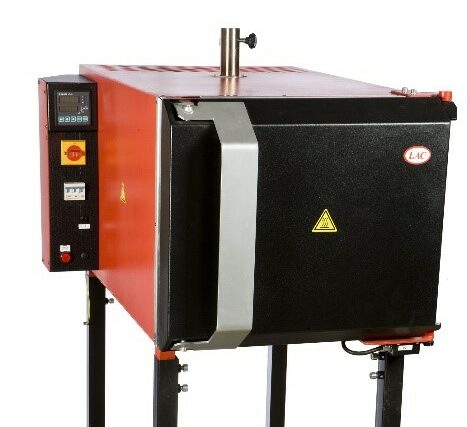
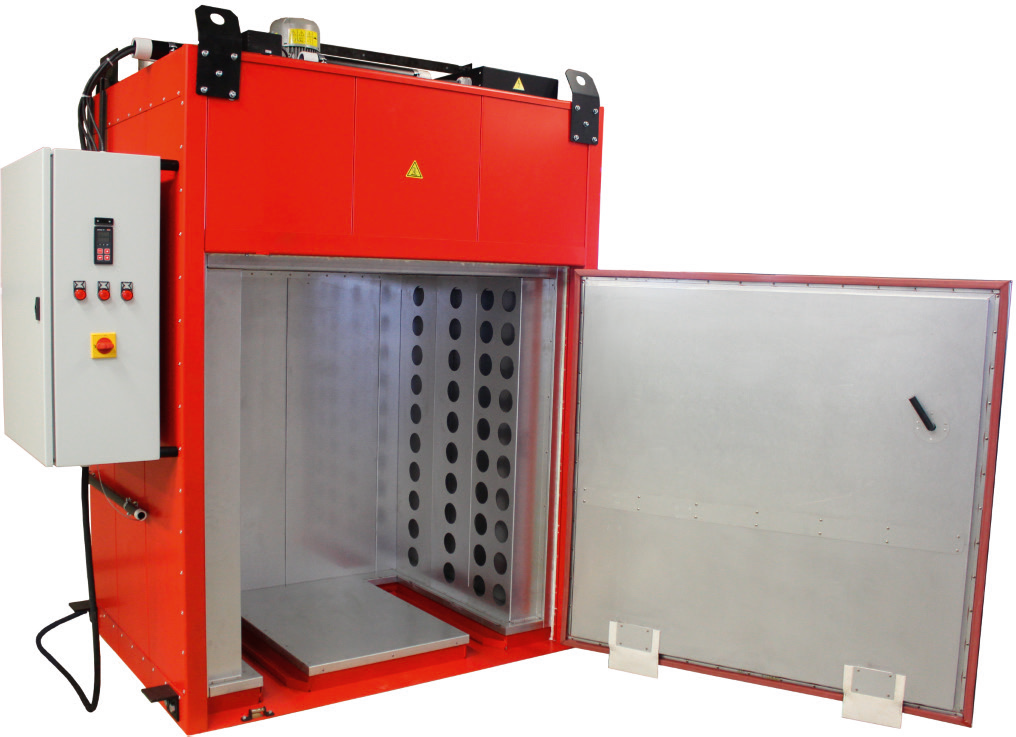
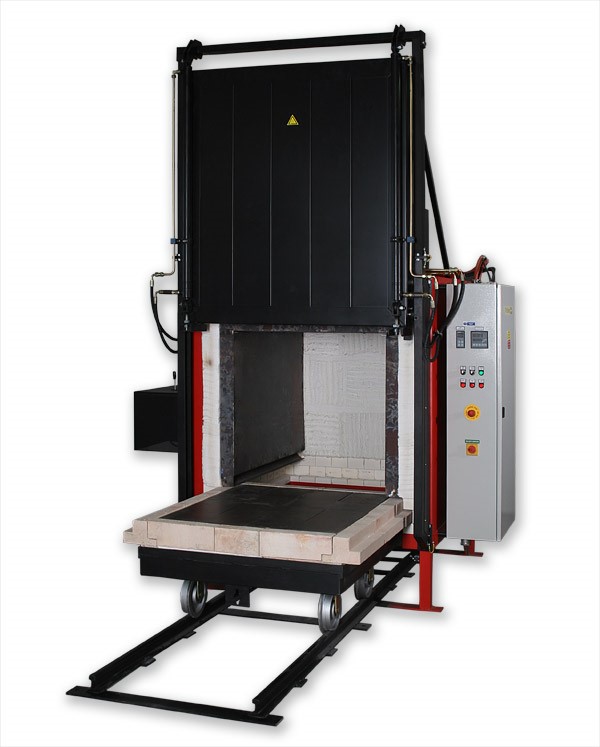
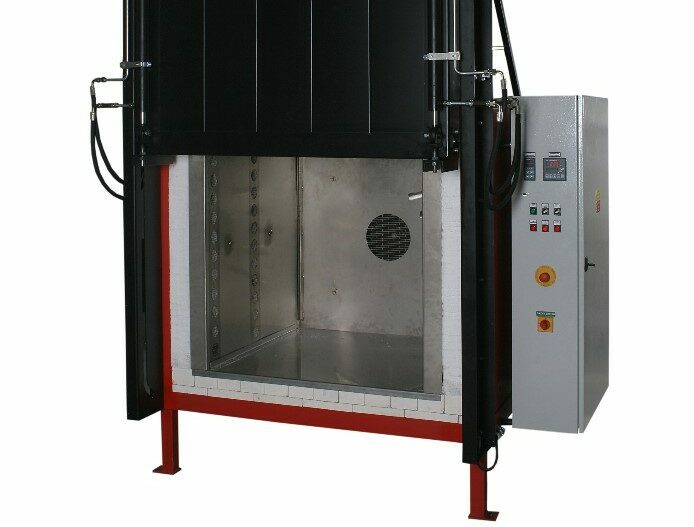
Convection furnace, hardening furnace or annealing furnace
Depending on the operating temperature, different variations of industrial furnace are used for this purpose. Air circulation ovens are often used in the temperature range up to 650°. In addition, annealing furnaces or hardening furnaces that work with radiant heat are often used.

 Deutsch
Deutsch


